A Deep Dive into Essential Control Panel Components
Control panels serve as the nervous system of industrial equipment as they are the central point of electrical distribution and control for machinery and processes in a manufacturing facility. Control panel components, such as fuses and circuit breakers, buttons, switches and other devices, enable operators to control, adjust and monitor the equipment that the control panels power and protect.
Understanding the role of essential control panel components is crucial for anyone who designs, operates or maintains control panels and helps ensure that these integral interfaces are safe, functional and reliable.
Types of Control Panels
Before exploring control panel components, it’s best to explore the different types of control panels found in industrial settings, including:
Industrial control panels
Designed for controlling automated equipment or processes in industrial facilities, an industrial control panel includes many of the same components as an electrical control panel but likely also contains programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and a human machine interface (HMI) that operators use to communicate with the machine or process.
Electrical control panels
Used to manage and control electrical devices in industrial facilities, electrical control panels typically contain fuses and circuit breakers, relays, transformers and the like.
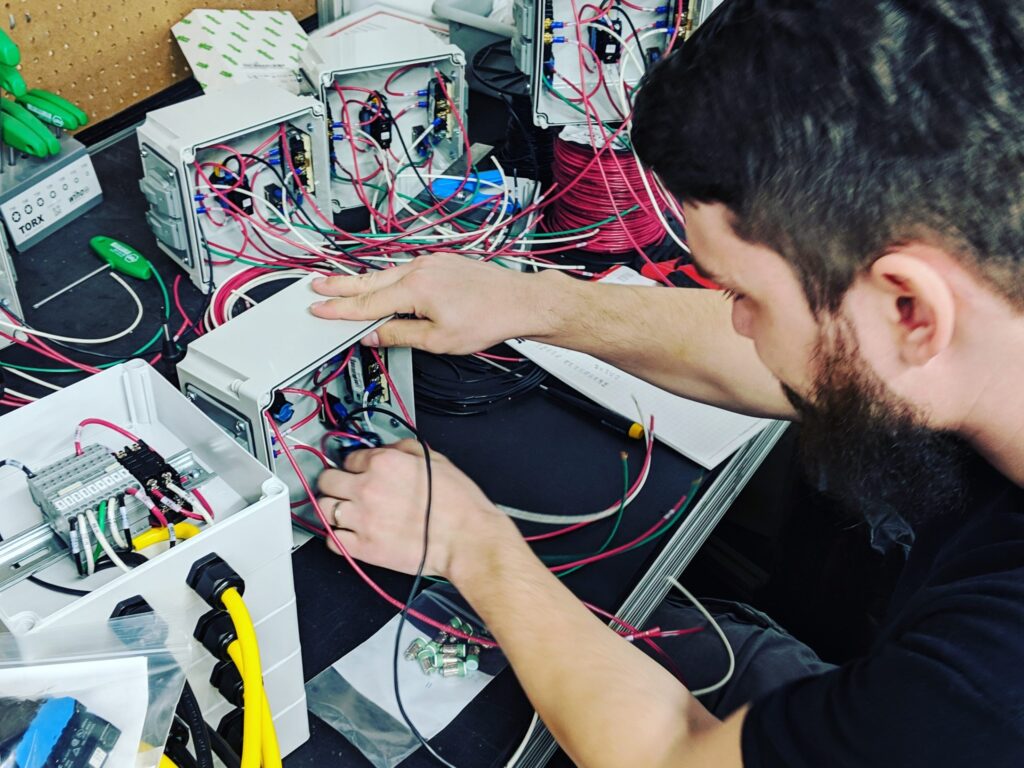
What’s Inside a Control Panel?
A well-designed and well-maintained control panel not only provides power to the equipment, but it can help maximize productivity and optimize control of the equipment or process, while also enhancing operator and facility safety. Understanding the purpose of each of the components housed within an electrical or industrial control panel is essential to safe and effective operations.
So without further preamble, here are the most common types of control panel components:
| Power supply | The power supply changes alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). DC is then supplied to the control panel and distributed to devices that require DC voltage. |
| Transformers | Used to manage the electrical voltage in a control panel, transformers match the level of voltage to the needs of the system, ensuring safety and performance of the equipment. |
| Terminal blocks | These control panel components provide a secure place for joining or consolidating wires from various parts of the system. They are helpful when troubleshooting or maintaining the control panel. |
| Switches | Switches allow operators to manually control the operation of industrial equipment and enable communication between components. |
| Relays | Relays are electrically operated switches that control large pieces of machinery or entire processes. |
| Contactors | These control devices manage large amounts of electrical current and may be used to switch loads on or off or provide protection against electrical overloads. |
| Indicators | Indicators provide visual information about machine status. Indicators may include lights that represent power status, alarms to alert operators to a problem or displays that convey data, such as temperature or speed. |
| Fuses and circuit breakers | These components are there to detect excess electrical current. Fuses will prevent overloading during periods of high current and must be replaced after being activated, whereas circuit breakers prevent short circuiting and overloading of connections by disrupting the connection to stop the flow of electricity. |
| Surge suppressors | These devices prevent short circuiting related to excess voltage,such as in the event of a lightning strike or power surge. |
| Motor drives and starters | These control panel components regulate the speed and torque of an electrical motor to provide precise control of machinery motors. VFDs, servo drives and soft starters are examples of motor drives. Motor starters combine a contactor and an overload relay to control the electrical output of a motor during start up. |
| PLCs | Found in some industrial control panels, programmable logic controllers are miniature computers that control automated manufacturing processes. They monitor the status of sensor inputs and use the information to control motors, valves and other essential equipment. |
| HMIs | In some industrial control panels, human machine interfaces provide information to operators and may also be used to control or adjust automated equipment or processes. |
| Ethernet switches | In industrial control panels that control automated equipment, Ethernet switches allow communication between the PLC, HMI and other smart/connect components. |
Electrical control panels and industrial control panels may contain just some or all of these components, depending on their application and function in the facility. Whether the control panel is simple or complex, understanding what’s inside will help operators better control the equipment and maintenance techs more easily troubleshoot and perform repairs. For assistance with designing, maintaining or installing a control panel or selecting control panel components, please contact PTS, a Tavoron company, today, because the right control panel and components can contribute to the effective performance and the safety of the equipment.
