The Role of Robotic Arms in Modern Manufacturing
Robotic arms serve as the highly efficient “hands” of automated machinery in manufacturing operations. Developed to make tasks that were previously managed by human employees significantly faster, more accurate, highly repeatable and safer when properly integrated, robotic arms have revolutionized the modern manufacturing industry.
This blog will explore the benefits and mechanics of robotic arms, as well as the most common types of robotic arms and their role in manufacturing.

Robotic Arm Advantages
Modern manufacturing operations rely on robotic arms to replace manual laborers in operations that may be to repetitive or risky for humans, tasks that require high speeds and/or extreme precision on production lines that demand continuous, 24/7 operation.
In these instances, the use of robotic arms provides many benefits, including:
- Increased throughput: The high speeds and ability to work without breaks allow robotic arms to increase efficiency, productivity and throughput on the production line.
- Improved quality: Because robotic arms can work at high speeds while maintaining precision and accuracy that exceed human capabilities and are programmed to repeat the same tasks in the same manner each time, they can enhance the quality of assembled components and finished products, while reducing wasted materials and labor hours spent on rework.
- Better use of labor: Robotic arms excel at performing repetitive, simple tasks that human employees find monotonous, as well as those that require higher levels of strength than human workers can provide, employing robotic arms in these situations frees up human laborers to perform higher-value, more complex tasks around the facility.
- Enhanced safety: Applying robotic arms to tasks that require repetitive bending, lifting and twisting motions, or those that take place in hazardous environments, safeguards human employees from repetitive motion injuries. Including those caused by working in dangerous areas. The use of automation reduces injuries and improve the safety record of the facility.
Modern Manufacturing Applications for Robotic Arms
Because robotic arms provide significant advantages for manufacturers and can be programmed to perform a variety of tasks, they are finding use in just about every application in modern manufacturing environments.
Some of the most popular applications for robotic arms include:
- Welding
- Placing components on a production line
- Inspecting or testing products for quality control
- Assembling components or products
- Picking products from a production line
- Material handling
- Painting and finishing
- Packing products into boxes
Exploring Robot Arm Mechanics and Types
The reason robotic arms are versatile enough to be adapted to these and other applications is because they offer the same motions as a human arm – only faster and with more precision – because the mechanics of a robotic arm include parts that simulate the action of a human shoulder, elbow and wrist, which all work together to coordinate movements.
Most types of robotic arms include the following components:
| Joints and actuators | Powered by electricity, pneumatics or hydraulics, actuators allow the joints of the robotic arm to bend, twist and turn to provide the necessary movements to complete a task. |
| Links | Links connect the robot’s joints and determine the reach of the robotic arm. |
| Sensors | Housed within the arm, sensors provide “awareness” to the robotic arm, so it knows the location of its joints, what direction they are moving and what action they are performing. |
| Controller | The controller “talks” to the robot and integrated system, guiding the activities of the robotic arm. |
| End of arm tooling | Designed for a particular task, end of arm tooling, end effectors or grippers serve as the “hand” at the end of the robotic arm. End of arm tooling is used to grasp, grip, pick up and otherwise manipulate the part, component or tool that the robotic arm must handle. A camera on a robotic arm can also be used for inspection. |
All of these parts come together to create a single arm with twisting joints. The resulting robotic arm is attached to a stable base that is situated within the work envelope. Depending on the type of robot, there are typically between four and six joints to provide enough flexibility to conduct the task at hand.
While there are many robotic arm types available, the following are widely used in modern manufacturing situations:
Cartesian robot arm: These arms are linear or gantry-style robots that work on three linear axes using the Cartesian coordinate system of X, Y and Z so they can move in a straight line among three different axes – up and down, in and out and side to side – and provide flexibility and agility.
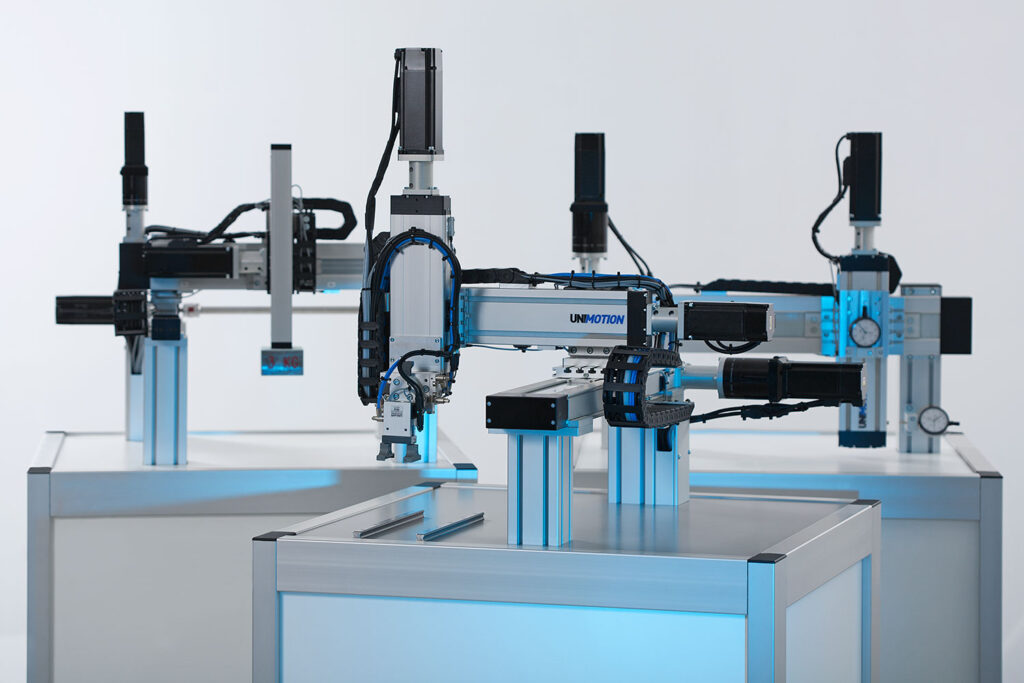
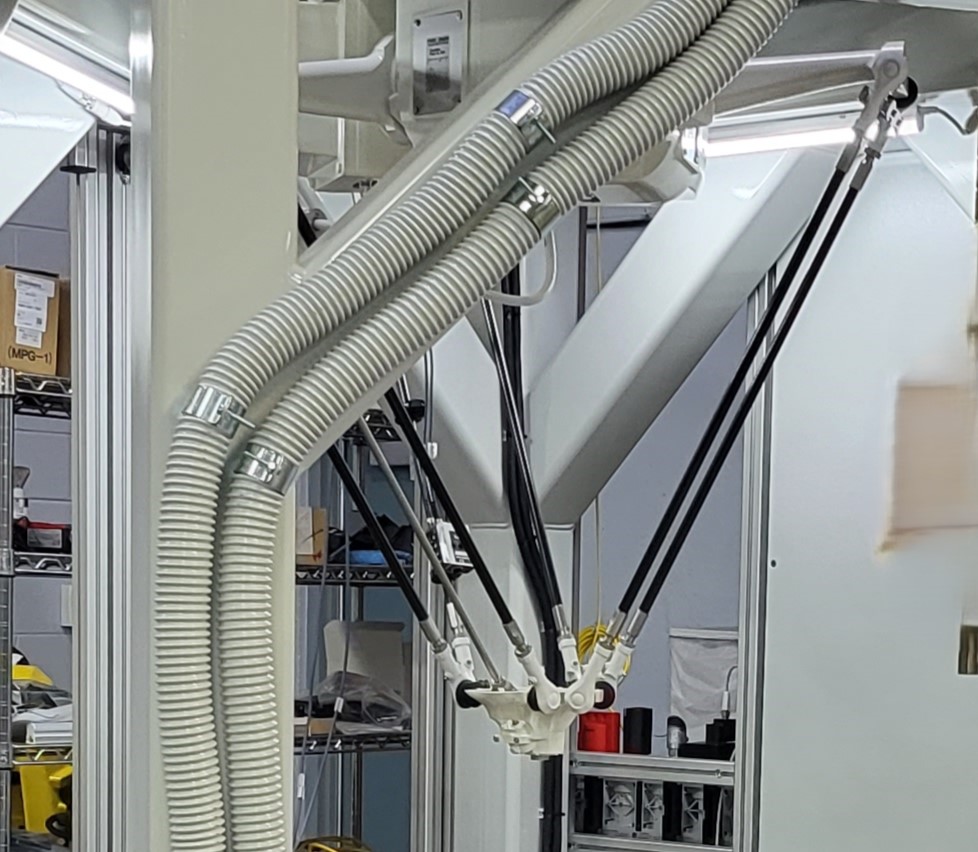


Delta robotic arm: Known for speed and accuracy, delta arms have three arms connected to one base.
SCARA robot arm: SCARA, or Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arms, can move in three directions and twist around, making them an excellent choice for high-speed, yet precise palletizing and assembly tasks.
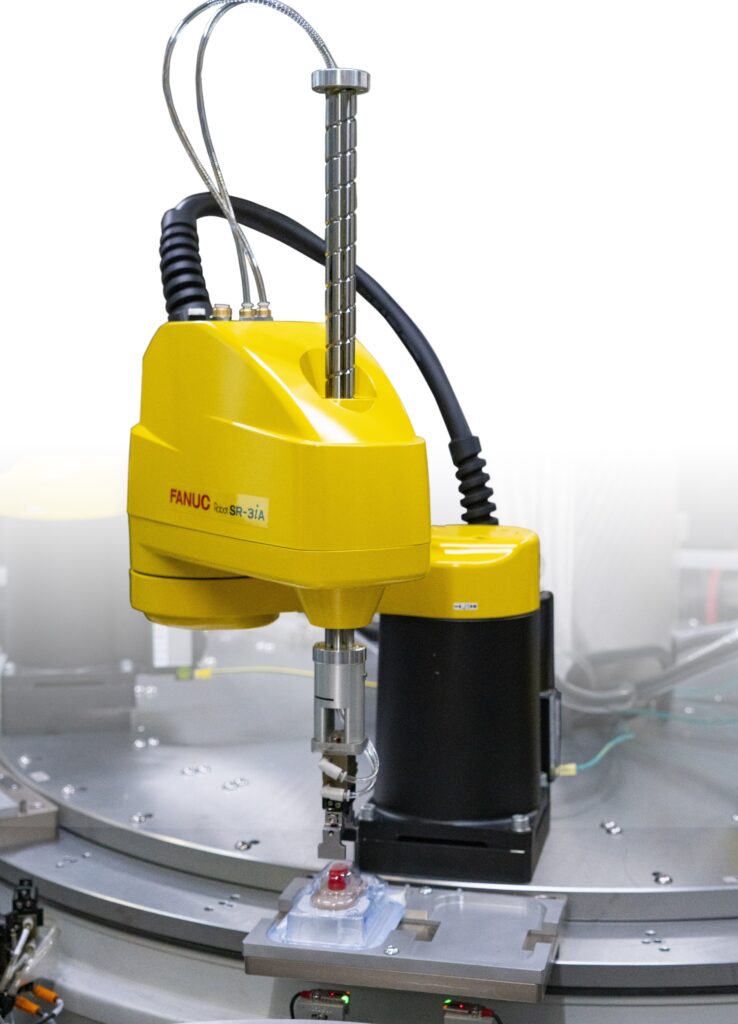


Cylindrical arms: This type of arm features a rotary joint at the base, enabling it to reach across the work envelope. The compact design makes cylindrical arms great for assembly and machine tending tasks.
Polar or spherical arms: These robotic arms offer an arm with a single joint that can move back and forth and two rotary joints that spin, creating a spherical work envelope that is suitable for welding and other tasks.
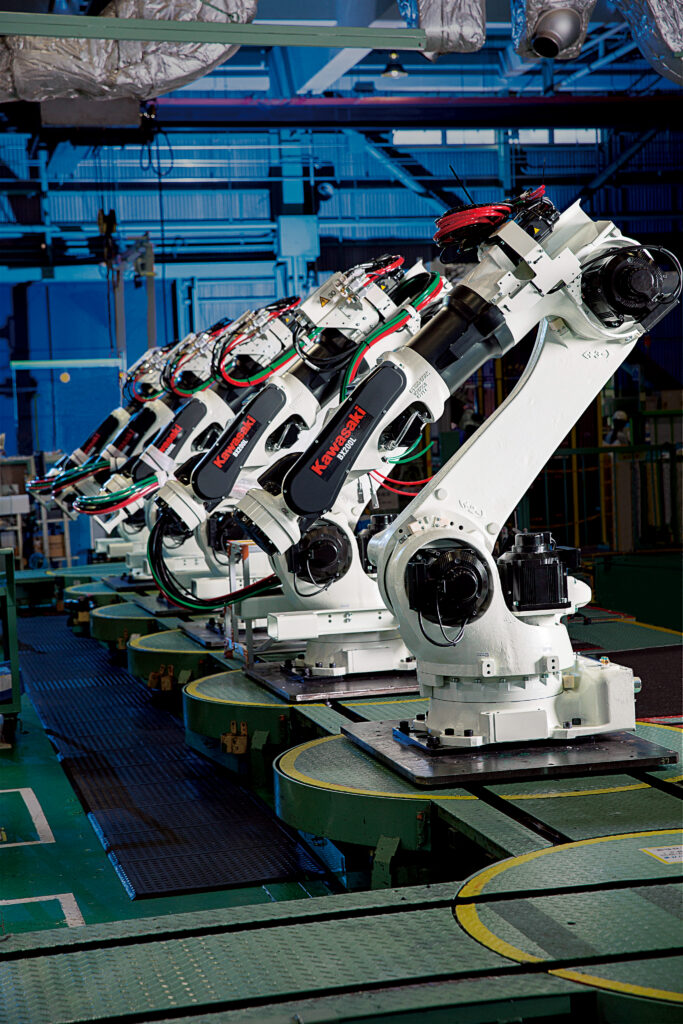
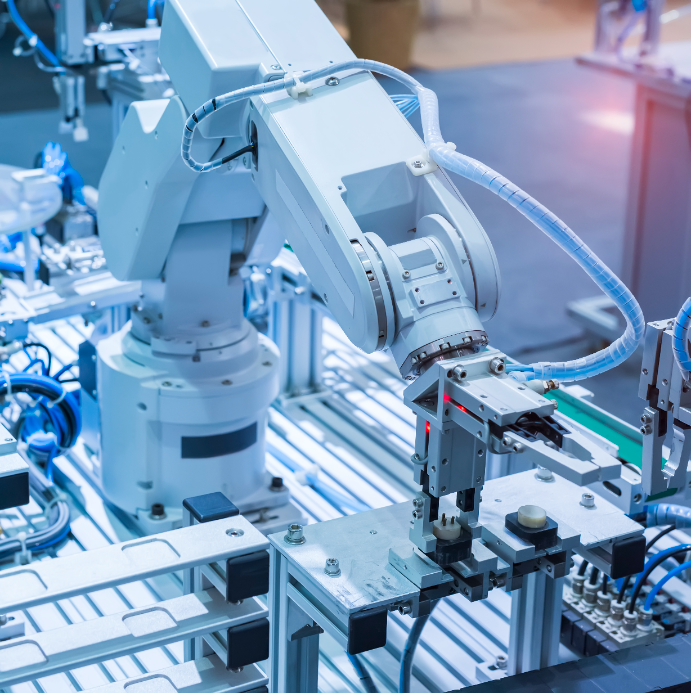

Articulated robot arms: The design of this articulated robotic arm most closely resembles that of a human arm, featuring a single mechanical arm attached to a base with a twisting joint. They typically offer between four and six axes to provide a wide range of motion and are suitable for almost any operation, including welding, painting, assembly, material handling and palletizing.
Due to their adaptability, high speeds and accuracy, robotic arms have become indispensable in modern, advanced manufacturing operations where they bring enhanced efficiency, quality and safety to any setting. To find out more about how robotic arms can effectively automate your production line, please contact JHFOSTER today.
