Linear Actuators Improve Medical Equipment and Patient Care
Through the years the medical industry has adopted new technologies in an effort to improve patient care and comfort. Linear actuators play a crucial role in many of these medical equipment advancements,
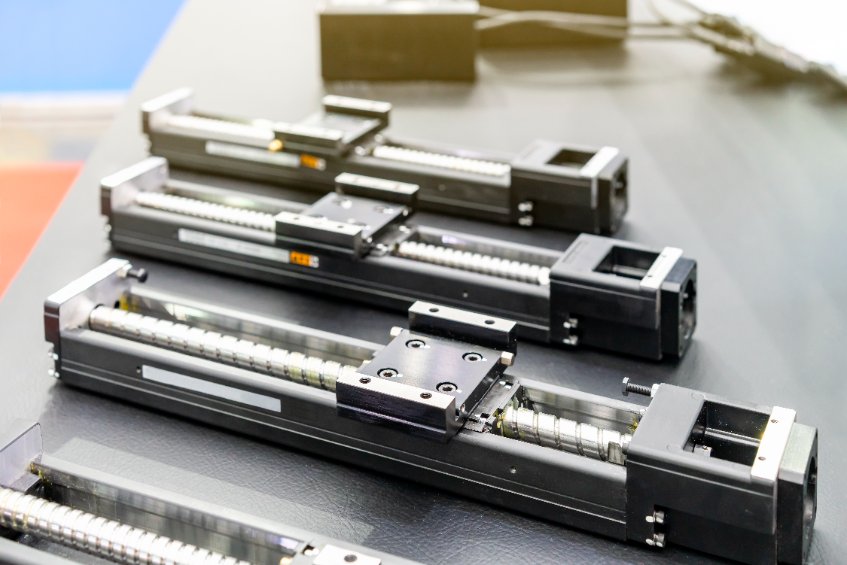

as they reliably complete the required lifting, tilting and straight-line motions necessary in today’s healthcare environments. In addition to easing the burden of moving patients without jostling them in applications such as hospital beds, wheelchair lifts and X-ray tables, linear actuators also contribute to the efficient, smooth, reliable and safe operation of life-enhancing medical equipment, such as diagnostic tools, surgical robots and prosthetic limbs.
What is a linear actuator?
A linear actuator is composed of a motor, gears and a screw or rack-and-pinion mechanism that work together to convert a source of power – either hydraulic, pneumatic or electric – into mechanical motion that moves in a straight, or linear, line. Electric linear actuators are most often the choice for medical equipment, so this article will focus on electric linear actuators.
Electric linear actuators use voltage and current to position a mechanism such as a ball screw or rack and pinion to convert the rotational force of an electric motor into a linear force. Because they use electricity as the power source, which is easier to control and more efficient than fluid or air, electric actuators provide more precise control of speed and force and better positional accuracy than air- or fluid-powered actuators. This enhanced precision and accuracy also mean that electric actuators are superior at repeating specific motion profiles without drifting. Advanced electric actuators may also offer data feedback, which helps them handle more complex motions, as well as multi-point positioning.
Why electric linear actuators are preferred in healthcare
In addition to the precise control of speed and force and excellent accuracy, electric linear actuators tend to be more reliable and provide smoother, cleaner and quieter motion than other types of linear actuators, making them the oft-preferred choice for medical equipment. Electric linear actuators are also the technology chosen for medical equipment because they operate at low voltages – typically between 12 and 36 volts – and offer lower speeds than their air- or fluid-powered counterparts, which helps ensure that patients are not jostled or moved too quickly. The lower sound volume produced by electric linear actuators is also appreciated in healthcare settings.
All of the positive attributes related to electric linear actuators combine to provide medical equipment that simplifies patient movement, allows medical staff easier and more efficient access to patients and helps improve the quality of care for patients in hospitals, diagnostic centers, nursing homes, treatment centers and home care settings.
Common medical equipment applications for electric linear actuators
When in a healthcare setting, most patients and staff don’t stop to think about how smoothly and easily the exam table adjusts or how accurately the infusion pump works, but if they did, the solution would likely include a linear or electric linear actuator. As a matter of fact, linear actuators are used in a wide array of medical equipment applications, including:
- Hospital beds: Hospital beds that allow patients and medical professionals to easily raise and lower the bed and reposition it at different angles for sitting and sleeping likely employ linear or electric linear actuators because they are quiet and reliable and offer smooth transitions between positions.
- Exam and X-ray tables: For the same reasons, linear or electric linear actuators are often used in the exam and X-ray tables found in doctor’s offices, hospitals and diagnostic centers where they reliably and smoothly elevate or move patients to the proper position for the exam.
- Incubators: Used in hospital nurseries, incubators rely on linear automation systems to properly orient the cradle and allow smooth and precise vertical adjustments to the incubator position for easier and more efficient patient care.
- Surgical theaters: In operating rooms, linear actuators are used to control straight line motion of surgery tables and positioning equipment to allow surgeons and nurses better, more comfortable access to the patients, which is especially important during long and complicated surgeries.
- Surgical and medical robots: Electric linear actuators in medical and surgical robots permit accurate, smooth, precise and well-controlled motion in delicate operations and procedures.
- X-ray and diagnostic machines: Linear actuators allow vertical movement and adjustment of X-ray machines, adjustment of mammography machines and the associated c-arms, CT scanners, MRI machines, PT scanning instruments and other diagnostic equipment. In these advanced imaging systems, electric linear actuators provide two benefits. First, they permit machines to be placed in the exact position necessary to capture the best images. Second, they provide precise, controlled motion, which allows clear images to be taken as any quick or jerky movements would cause image blurring, making results difficult to interpret.
- Rehabilitation equipment: In machines used during patient rehabilitation, such as motorized chairs, the reliable and smooth linear movements provided by linear actuators help regulate the height of the seat, backrests and footrests. Linear actuators are also used in stair lifts to open and close the final section of the rail. The use of linear actuators in these types of equipment enable patient comfort and independence.
- Infusion pumps: Syringe pumps and small infusion pumps used to gradually administer intravenous medications to patients or to control small amounts of fluids in laboratory or research settings often include small, specialized electric linear actuators because they offer the precision, accuracy and repeatability that are necessary to these demanding applications.
The above-mentioned applications only skim the surface of the use of linear actuators and electric linear actuators in medical applications. They can also be found in prosthetic limbs to allow smooth, quiet motion; other medical testing devices to provide positional precision; valve and pump actuation to allow accurate dosing; positioning devices for dental tools; locking mechanisms for vehicle-mounted wheelchair lifts; and many others.
For information on selecting the right linear actuator for a medical device, machine or equipment, please contact a specialist at JHFOSTER.