How To Choose A Proportional Valve For Medical Devices
Choosing a valve for medical devices is crucially important in facilitating quality patient care. The correct valve can make the difference in providing life-supporting treatment or causing problematic complications. Solenoid valves are typically used for medical devices because they can moderate gas flow with precise speed and accuracy to support patient care. When used in the delivery of oxygen, for example, the valve is used to achieve the correct concentration of gas, and to control the rate of oxygen flow to the patient.
Consisting of an electric coil which surrounds an iron core, a solenoid valve is powered using electricity. It converts this electrical energy into a linear motion, opening or closing the valve, thereby enabling medical personnel to precisely control the flow, direction and pressure of fluids or gases.
Proportional Valve Overview
Medical solenoid valve applications demand high accuracy in terms of force and stroke. They come in several configurations which can be used to act as a shut off, or to allow for two paths of flow. A dialysis machine, for example, uses two solenoid valves acting in tandem to control blood flow during the cleansing process.
While most valves operate in a simple on/off state, a proportional solenoid valve is a precise variation which provides a change in output in the same ratio as the change in the input. If the input doubles, for example, then the output will double as well. In a medical environment where plumbed air is provided, there can be troublesome fluctuations in air pressure which might cause equipment malfunctions.
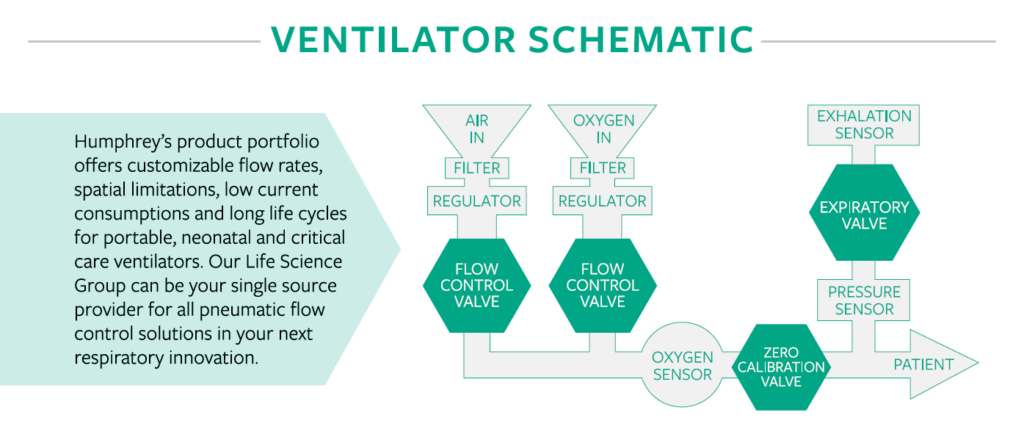
A ventilator, for example, requires a high flow rate of oxygen and air, but often relies on the relatively low supply pressure of the plumbed supply. The proportional valve is used in these situations to control fluctuations, and maintain a balanced airflow for the patient.
Proportional solenoid valves regulate flow rate by varying the position of the valve plunger. Typical medical applications where a proportional valve is used to deliver precise performance in pressure or flow applications might include:
- Delivering anesthesia during surgery
- Mixing and controlling delivery of ventilator and respirator gases
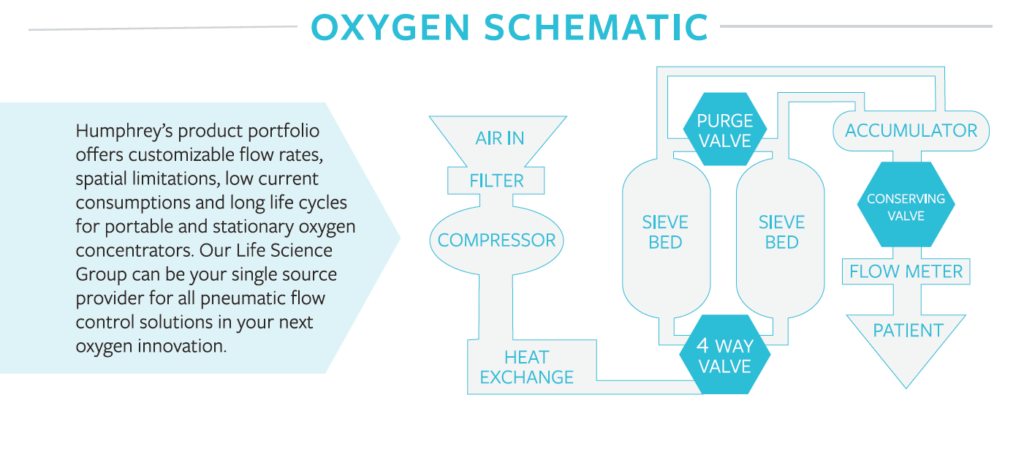
- Oxygen concentrators
- Positive End Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) to maintain pressure on the lower airways at the end of the breathing cycle
- Shock wave therapy
- Surgical instruments
- Patient monitoring devices
- Medical mattresses
Variable control methods offered by proportional valves include:
- Dynamic Control: This is used when continuous high-frequency adjustments are required.
- Incremental Control: Appropriate when there are pre-determined, low-frequency adjustments required within each cycle.
- Selectable Control: Allows for selected output flow per cycle, as needed.
How To Find A Proportional Valve
Proportional valves are used in the medical device sector because they offer the right capability range, and adequately serve most medical device applications. Variables involved in choosing a proportional valve for medical devices include:
- Device Specifics: What type of device needs a valve? What does it do for the patient? How big is it? Does it need to run continuously, or for specific periods of time?
- Medium: The requirement for liquid or gas to flow through the valve will be an influencing factor in setting valve construction criteria.
- Variables: A proportional valve can control many variables, such as force, pressure and flow. Specify exactly what the valve will be expected to accomplish.
- Adjustment Periods: Some systems require constant flow and pressure while others change quite frequently, which requires more adaptations on the part of the proportional valve. A ventilator requires constant adjustments to produce the appropriate gas mixture for delivery to the patient.
- Pressure: Consider the incoming pressure source, and maximum controlled output pressure requirements.
- Flow: Required flow range for specific medical application.
- Temperature: Ambient temperature requirements.
- Power: Look at power capabilities, especially in terms of mobile or portable applications.
- Environmental Factors: What is the location of the medical device? Are there any space or weight constraints? Is portability a requirement?
- Compliance: In the medical field, there may be special requirements related to medical devices in order to comply with FDA or other regulatory requirements.
While some medical devices are constantly monitored, others are expected to perform consistently and reliably on an autonomous basis. Proper proportional valve selection is crucial for their operation. Contact JHFOSTER today to receive information and guidance from our team of experts, and let one of our certified technicians walk you through deciding which proportional valve is right for your specific medical application.
Headquartered in Eagan, Minnesota, JHFOSTER provides a wide range of reliable pneumatic valves for an array of applications. The JHFOSTER team can be your partner in choosing the right components, in the right systems, for your specific medical device applications. Contact us online, request a quote, or call 855-688-0043 today to discuss which proportional valve is best suited to your medical device needs.