Cost-Effective Machining Robots Offer Flexibility and Enhanced Productivity
Machining is a manufacturing process where raw materials are cut into specific sizes and shapes using a controlled material removal device. While activities such as trimming, drilling, milling, welding, grinding, deburring and polishing can be performed manually, automating machine tasks can provide significant efficiency and throughput advantages for manufacturers. Although automated machining has traditionally been performed via computer numerical controlled (CNC) machines, the cost effectiveness and flexibility provided by machining robots makes them a viable alternative in modern manufacturing facilities that are looking to increase productivity and gain a competitive advantage.
Machining Robots Explained
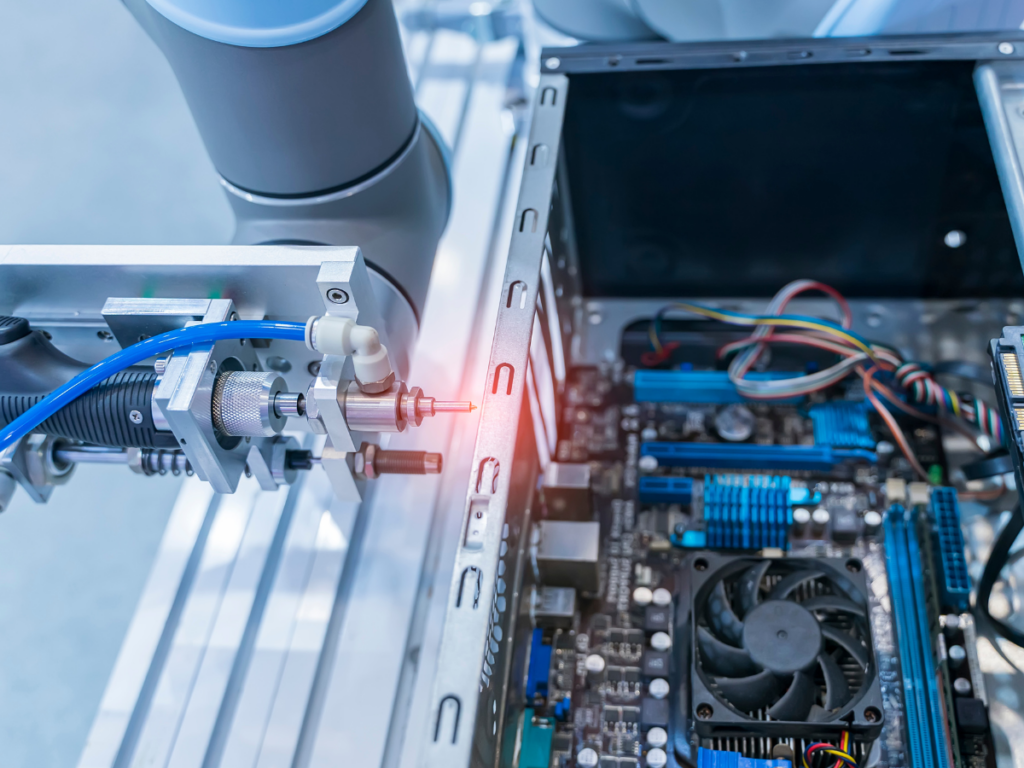
Robotic machining is the process of using automation and robots equipped with various tools such as end mills, drills or grinders to perform machining activities such as milling, drilling, cutting, grinding and polishing. Today’s machining robots are programmed to move along a predetermined path to perform machining operations.
While CNC machines were previously the gold standard for automating these activities,
many manufacturers are finding that modern machining robots can perform the same machining operations at a lower cost and with greater flexibility.
While they serve the same purpose of manipulating raw materials, CNC machines, which follow a pre-programmed code to process the raw materials, are generally only able to perform one specific task and have small workspaces. Machining robots, on the other hand, are reprogrammable and can, therefore, perform a variety of activities. They also offer larger work envelopes and more degrees of freedom, allowing them to operate over larger areas and work on larger pieces. Another major difference is that CNC machines are typically more rigid than machining robots, so they excel at machining hard materials, while machining robots provide an accurate, flexible and cost-effective choice for machining softer materials such as plastic, aluminum or wood.
5 Major Advantages of Machining Robots
As more manufacturers look into the use of machining robots, they find that they offer several unique advantages, including:
- Flexibility: While CNC machines typically perform only one task, machining robots can automate multiple applications, such as picking a workpiece, placing it and then processing it, making them versatile. They are also easily reprogrammed and a variety of end effectors and tools can also be added allowing flexibility and providing manufacturers with a high level of adaptability, which is essential when dealing with variable or short production runs and peak demand periods.
- Lower Rigidity: Even though machining robots offer lower rigidity than a CNC machine, they can provide great accuracy and precision when cutting softer materials such as wood, plastic, foam and aluminum. Additionally, in applications such as polishing and sanding, the lower rigidity of machining robots prevents scratching of uneven surfaces. The accuracy and precision in these types of applications helps increase quality and reduces waste.
- Larger Workspaces & More Degrees of Freedom: Machines with more degrees of freedom are capable of making more complex motions and, because machining robots have larger workspaces, more axes can be added to a robot to extend the workspace. This is particularly important when a broad reach is required, such as when deburring or polishing large pieces or removing rust from large metal sheets before cutting.
- Higher Productivity: Because machining robots are versatile and capable of performing several functions, such as placing a workpiece and then cutting it, with precision and high speed, they can significantly increase the productivity, efficiency and throughput of a process. Additionally, they can be programmed to work without breaks or human intervention 24/7, further increasing productivity and reducing labor hours and costs.
- Cost Effective: As robotic technology continues to advance and permeate the industrial space, machining robots are becoming more price competitive with traditional machine tools. Further, when higher productivity and reduced labor costs are factored into the equation, machining robots prove to be incredibly cost effective. In addition, the ability to perform multiple tasks and be reprogrammed to perform different applications provides a lot of value to manufacturers that have shorter or variable production runs.
Robots for Machining
Several types of robots may be adapted to perform robotic machining. The most commonly used robots for automating machining activities include:
| Cartesian | Articulated Robots | SCARA Robots | Collaborative Robots |
| Because Cartesian, or gantry robots, operate in the Cartesian plane on the x, y and z axes, they excel in applications that require pick and place and simple machining operations that move in a straight line. | With multiple rotary axes, articulated robots offer a range of motion similar to that of the human arm, making them suitable for tasks that require complex motion, such as welding. | The horizontal arm of a SCARA robot permits accuracy and high speeds, making them suitable for applications that require high throughput and precision. | Cobots are well suited to tasks that require repetitive, human-assisted motions in small areas. Because they are designed with safety features that allow them to work in areas where they will encounter human workers, they are an ideal choice for busy manufacturing floors. |
When considering whether a machining robot is the right choice for automating a machining operation, it’s important to take into consideration the specifications of the application and raw material being processed, as well as the flexibility required now and in the future. A risk assessment also needs to be performed to assure safety requirements and standards are met. Under the right circumstances, machining robots provide a versatile, accurate and cost-effective way to increase the efficiency and throughput of machining operations, which can provide a significant competitive advantage for today’s manufacturers. For assistance selecting a machining robot, please contact JHFoster.
